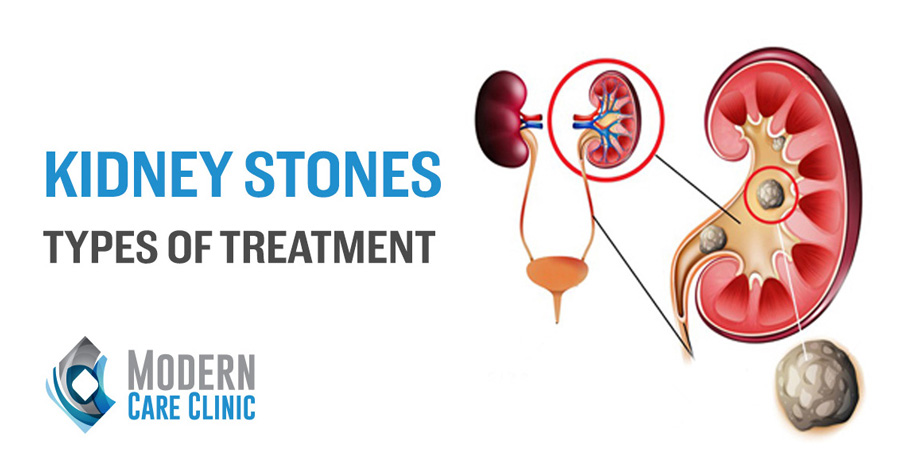
UTIs in women
Diagnosis of UTIs in women
First, the doctor will ask about the symptoms and the sexual activity of the patient; a urine analysis and urine culture will be required to prove the infection and determine the nature of the bacteria.
In case of recurrent UTIs, a doctor may request further diagnostic testing to determine the cause:
Diagnostic imaging: to assess the urinary tract by using ultrasound, CT and MRI scanning, radiation tracking, or X-rays.
Cystoscopy: This diagnostic exam helps the doctor to examine the lining of your bladder with a camera lens, which inserted through the urethra through a long thin tube.
Treatment of UTIs in women
-Antibiotic: The patient will probably start taking the antibiotic before getting the results of his urine test.
When the results (accompanied by an antibiogram) are done, your doctor may change the prescription if the test shows that the bacteria causing your UTI is resistant to this antibiotic.
-Medications for pain relief.
-Drinking lots of water.
-Urinating frequently.
If the infection is not treated, it can lead to kidney damage.
In case of recurrent infections in women:
-Take a single dose of an antibiotic after sexual intercourse.
-Take a single, daily dose of an antibiotic for 6 months.
-Undergo estrogen therapy in case of menopause especially put vaginal eggs.
Some TIPS to reduce the risk of UTIs in women:
-Drink lots of water and urinate frequently.
-Reduce the quantity of alcohol and caffeine.
-Urinate directly after sexual intercourse.
-Wipe from front to back after urinating and defecating.
-Maintain good personal hygiene of the genital area.
-Sanitary pads or menstrual cups are preferred to tampons. Avoid using a diaphragm or spermicide for birth control.
-Not use any perfumed product in the genital area.
-Wear cotton underwear.