Penile prosthesis
Definition
A penile prosthesis or Penile Implant is the best surgery that helps men with erectile dysfunctions when other treatments failed.
This procedure involves placing a prosthetic device or penile implant inside the penis and scrotum; so the patient can get a sufficient erection for sexual activities. And it lasts for 45 minutes to 1 hour under general or spinal anesthesia.
Penile implants are required when the medications are not efficient, and in some severe cases like Peyronie’s disease (fibrous scar tissue that develops on the penis and causes curved painful erections).
Follow the link for more information about Erectile Dysfunction.
Types of penile implants:
The patient should speak with his urologist to determine which implant is the best for him.
|
Type of penile implant |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Three-piece inflatable |
-Natural and rigid erection. -Provides flaccidity when deflated.
|
-The implant may sometimes not be effective (because of the large number of its parts). -Requires the presence of a reservoir in the abdomen.
|
|
Two-piece inflatable |
-Provides flaccidity when deflated. -The fluid reservoir is part of the pump. |
-The erection is not firm enough. |
|
Semirigid rod |
-Low chance of malfunction. ( due to the absence of the reservoir and the pump) – Easy to use. |
-Can be difficult to conceal under clothing. -a penis that is always slightly rigid. -possible difficulty with urination. |
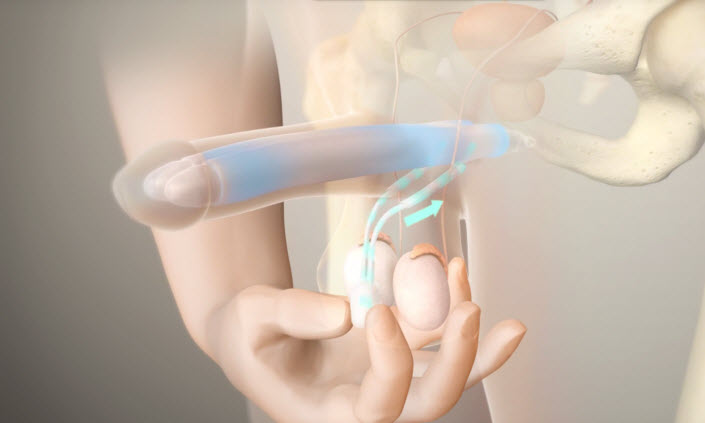
The inflatable implants required a pump inside the scrotum; so the patient should squeeze the pump to achieve an erection; the pump is located under the loose skin of the scrotal sac, between the testicles.
The device contains two chambers, and when the chambers are inflated by the pump; the patient then has an erection; when the patient is finished, he can deflate the device.
Follow the link for more details about the types of penile implants.
Which type of implant does the doctor choose?
There are several factors that the doctor put into consideration before deciding which implant will be the most suitable, including:
-The age of the man.
-Size of the penis, glans, and scrotum.
-Any history of previous abdominal or pelvic surgery.
-The presence of colostomy.
-A history of a kidney transplant.
-Whether or not the penis is circumcised.
-Health and well-being.
Penile implants don’t increase sexual desire or sensation.
Who should not get an implant?
-patient with uncontrolled diabetes.
-presence of a pulmonary or urinary infection.
-bladder obstruction
-when the erectile dysfunction is the result of a relationship conflict (the cause should be medical).
Penile implant = LOW RISK
– Low risk of infection (1-3%).
-low risk of mechanical failure (95% working at 5 years).
Some TIPS before and after the surgery
Before the surgery you should:
– stop taking aspirin and anti-inflammatory drugs before 7 to 10 days.
– Stop eating or drinking after midnight before your surgery.
– Shave the surgery site.
After the surgery:
– Physical and sexual activities can be resumed after 4 or 6 weeks.
-the patient should take an antibiotic to prevent infection; and medications to ease the pain.
– You should call your doctor if:
fresh and ongoing bleeding, significant discoloration of the penis, high fever, unable to urinate, cannot control pain, spreading redness, continuous drainage from the wound, progressive swelling of the penis, scrotum, or incision site.
Is the Prosthesis noticeable?
Men who have undergone the prosthesis surgery can notice the small surgical scar where the bottom of the penis meets the scrotal sac, or in the lower abdomen just above the penis, other people probably will be unable to know that a penile implant exists.
Finally, we believe that the penile implant is effective in its ability to restore the patient’s capacity to engage in sexual activities and regain what was lost due to a medical issue.
And the patient should not forget that ejaculation is not affected by this procedure.