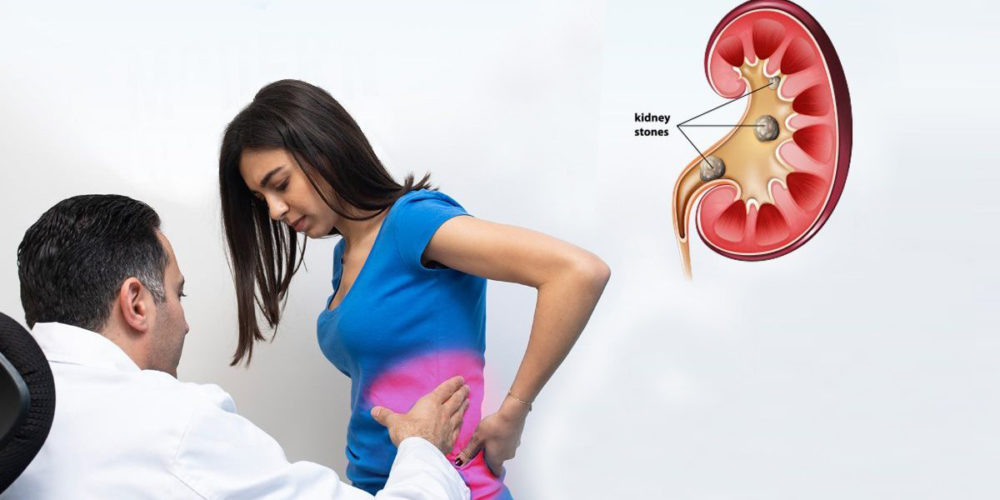
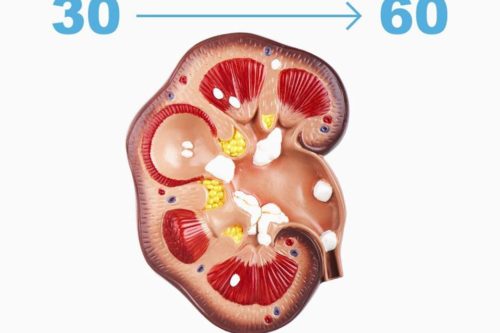
Kidney stones are hard solid mass of minerals and salts that form inside your kidneys.
Kidney stones form when minerals or acid salts in your urine form crystals and can appear in any part of your urinary tract.
Diet, dehydration, excess body weight, some medical conditions, family or personal history and certain supplements and medications are among the many causes of kidney stones.
Symptoms :
Symptoms depend on the size, shape and location of the stones.
A kidney stone will not cause symptoms until it moves around within your kidney or passes into your ureters.
If the stones block the flow of urine, the patient will present several symptoms:
-Renal colic (it is an emergency): Renal colic is caused when the stone blocks the normal urine flow through the ureter. It can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, blood in the urine, painful urination and fever.
-Dull pain: is caused when the stones didn’t block the ureter completely.
Diagnosis of kidney stones :
-Medical history and physical examination
-blood testing
-urine testing
-imaging techniques: ultrasonography , CT-scan (gives more details about the size, shape and density of the stone )
A metabolic evaluation is done if the patient have a high risk of forming more stones in future.
Treatment: depend on the symptoms, stone characteristics and the medical history of the patient.
The bigger the stone, the smaller the chance of passing it – the closer the stone is to the bladder the higher the chance of passing it.
-small stones with minimal symptoms can pass in the urine without invasive treatment; the doctor treat the patient by giving a medication like alpha blocker and a pain reliever and by telling him to drink a lot of water.
-large stones with symptoms: when the stone continues to grow and causes severe pain ; an active treatment in necessary ( a surgical treatment): uteroscopy, percutaneous nephrolithomy, parathyroid gland surgery, and shock wave lithostripsy by using sound waves to break up stones.
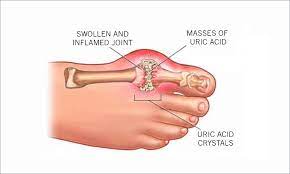
Type of stones: calcium stones, oxalate stones, phosphate stones, uric acid stones, ammonium urate stones, stuvite stones, cystine stones, infection stones and others…
To reduce your risk of kidney stones you should:
– drink enough water in the day
-have a balanced and varied diet (eat fewer oxalate-rich foods; choose a diet low in salt and animal protein; continue eating calcium-rich foods, but use caution with calcium supplements)
-adopting a healthy lifestyle
For more details about treatment of kidney stones, follow the link.