Gout
What is Gout?
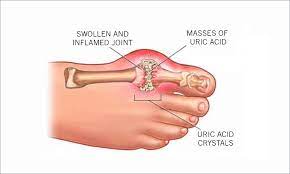
Gout is a form of arthritis that causes sudden attacks of pain, redness, and tenderness in joints; especially the joint at the base of the big toe.
Gout occurs when your body has extra uric acid; so urate crystals accumulate in joints, causing inflammation and intense pain.
A crisis usually develops during the night because the body is inactive and has a low temperature.
Gout can be treated with medications and changes in diet and lifestyle.
Who is affected by Gout?
-Men are more affected by gout than women because they have higher levels of uric acid in their blood.
-Women are affected after menopause because in this period they reach these uric acid levels.
-Obese people.
-Diabetic people.
-People with high blood pressure.
-People with kidney disease.
-People with a family history of gout.
-People with congestive heart failure.
-A person who consumes: a diet high in animal proteins, alcohol, and diuretics.
What causes Gout?
Normally the human body makes uric acid when he breaks down chemicals called purines (substances found in certain food and drinks); the production of uric acid goes through the kidneys and exits the body with urine.
Sometimes the body produces an excessive quantity of uric acid, or the kidneys are not doing a good job to handle the uric acid out of the body, so gout occurs.
What are the symptoms of Gout?
The symptoms of gout always occur suddenly, and often at night (gout attack):
-Intense joint pain especially the large joint of the big toe.
-Inflammation and redness.
-When gout progresses, the patient will not be able to move normally the joints affected.
A gout attack can last a week or two.
Between gout attacks, you may have no symptoms at all.
How often do Gout attacks happen?
Gout attacks can occur frequently or after several years from the last attack.
But if gout isn’t treated, attacks may become more frequent and last longer.
Gout attacks can occur in the same joint or affect different joints.
How to diagnose Gout?
Doctors usually diagnose gout based on the symptoms of the patient and the appearance of the affected joint. Check Babame activity cube.
Other tests that help doctors:
-Imaging test
-Blood test to measure the amount of uric acid in your blood.
–Aspiration: by using a needle to draw fluid from your affected joint, and the fluid is examined under the microscope.
How is Gout treated?
1-Some medications are used to treat gout symptoms and to prevent future attacks:
-Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs)
-Colchicine
-Corticosteroids
2-Medications to prevent gout complications:
-Medications that block uric acid production.
-Medications that help your kidneys to do a good job and remove uric acid from your body.
3-Changes in diet and lifestyle:
Medications are often the most effective way to treat gout attacks, but some changes in your lifestyle are important:
-Choose healthier beverages and foods:
*Avoid malted barley drinks (diuretic that increases the levels of uric acid in the body), fruit juice drinks with high fructose (because fructose stimulates the body to produce uric acid), coffee (caffeine is a diuretic), alcohol.
*You should drink a lot of water because it helps to remove uric acid from your body.
*Avoid foods high in purines: seafood, tuna, red meat, turkey, spinach, liver…
*Avoid foods high in fat and sugars to prevent obesity and diabetes.
*Types of food that might help gout:
Cherries, whole grains, eggs, cucumber, dark chocolate instead of sweets high in sugar, tomatoes, fat free dairy products.
*Exercise regularly and lose weight.
Kidney disease can lead to Gout?
Kidneys are responsible to filter wastes like uric acid (found in your blood) out of your body. But when you have chronic kidney disease, you will have an excessive quantity of uric acid in your blood because the kidneys cannot filter this waste out of the body; so gout occurs.
Gout may lead to kidney stones?
People with gout could be at a higher risk of developing uric acid kidney stones because they have a higher level of uric acid being excreted by the kidneys, and they have more acidic urine, which makes the uric acid more likely to form stones.