Varicoceles
What are varicoceles?
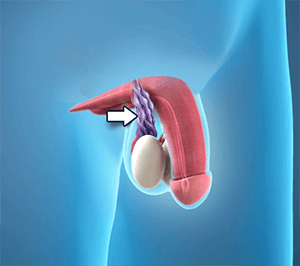
Varicoceles are when veins called pampiniform plexus become enlarged inside your scrotum (the sac that protects and holds the testicles). About ten to fifteen males out of one hundred have varicocele; it is like getting a varicose vein in your leg.
This condition is most common in young men; and affects the left side of the scrotum more than the right side, because the male anatomy is not the same on both sides.
Varicoceles can be on both sides at the same time, but this is rare.
What are the causes of varicoceles?
Your spermatic cord (each testicle is holding up by a spermatic cord) transfers blood to and from your testicles.
It’s not certain what causes varicoceles; but the principal cause could be a problem with blood flow in the spermatic cord.
Many experts believe a varicocele forms when the valves inside the veins in the cord prevent your blood from flowing properly; which leads the veins to dilate. This might cause damage to the testicle and lead to infertility.
When varicocele occurs in puberty, it’s often because of the immediate growth they undergo during puberty. The testicles need more blood than normal as they develop, and any problem in the veins can keep the blood from getting where it needs to go.
What are the symptoms of varicoceles?
Varicoceles often don’t present symptoms; but sometimes you may notice:
• Dull testicular pain or scrotal aching; which often gets better when you lie down, and get worse while doing certain activities.
• Inflamed testicle or scrotum.
• Male infertility.
• Sensation of a mass above the affected testicle.
• Enlarged veins that are quite noticeable.
Complications
• Testicular atrophy: The majority of the testicle comprises sperm-producing tubules. When damaged, as from varicocele, the testicle contracts and softens. We can’t explain why the testicle shrinks, but the malfunctioning valves allow blood to pool in the veins, which can result in increased pressure in the veins and exposure to toxins in the blood that may cause testicular damage.
• Infertility: Temperature changes inside the scrotum due to blood accumulation in veins; this higher temperature may affect sperm formation, movement (motility), and function.
Diagnosis
In the physical exam, the doctor can feel above your enlarged testicle a mass that does not trigger discomfort upon palpation.
If you have a large varicocele, your doctor might ask you to stand, take a deep breath and hold it while you bear down (Valsalva maneuver); this helps your doctor detect abnormal amplification of the veins.
Sometimes the physical exam is inconvincing, so your doctor might order a scrotal ultrasound (a test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create precise images of the male’s testicles and surrounding tissues). In certain cases, other imaging might be recommended to rule out other causes for the varicocele, such as a tumor compressing the spermatic vein.
The size of the mass in your testicle helps your doctor classify your varicocele on a grading scale of 0-3.
A Grade 0 is the smallest, and can be diagnosed only with the help of an ultrasound.
Grade 3 is the largest, and means your varicocele is big enough that it changes the shape of your scrotum and can be diagnosed with the physical exam.
How to treat varicoceles?
Varicoceles require treatment only if:
• You have pain
• You have problems with your fertility
• Your right testicle is growing more than the left
There are no medicines to prevent or treat varicoceles.
If you do need treatment, the goal will be to remove the veins that supply blood to your spermatic cord. You might have:
Varicocelectomy: This surgery is performed to remove enlarged veins in your scrotum; and to restore proper blood flow to your reproductive organs, under local or general anesthesia through a small cut into your scrotum.
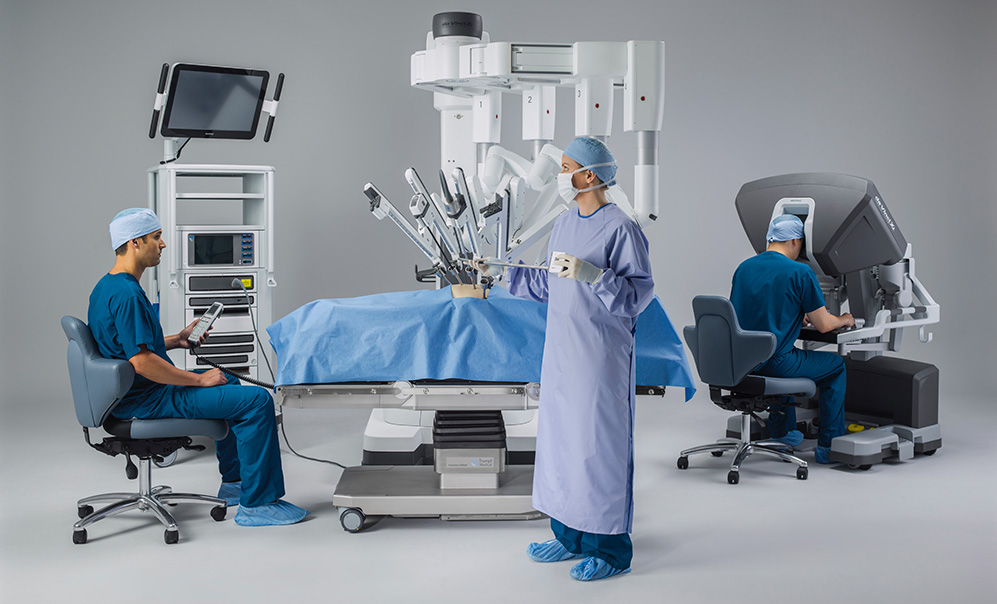
Laparoscopic surgery: The doctor makes a small incision in your abdomen and passes a tiny instrument through the incision to see and repair the varicocele; this procedure requires general anesthesia.
After those two surgical treatments, you may notice:
• Varicoceles don’t go away, or come back
• Hydrocele
• Your testicular artery gets injured
Percutaneous embolization: A radiologist inserts a tube into a vein in your groin or neck through which instruments can be passed; the radiologist inserts a coil by using X-rays, to deflect blood away from the enlarged vein in your scrotum, under general anesthesia.
Risks that can follow this procedure include:
• Varicoceles don’t go away, or comes back
• The coil moves
• An infection
Recovery
After embolization, you can return to work after two days, and begin exercising after seven to 10 days.
If you have the procedure to help with fertility, the doctor will test you in 3-4 months; that’s how long it takes for new sperm to grow. You’ll probably see improvements in 6 months, but it could take a year.
A little more than half of the infertile men who have the procedure benefit from it. Surgery is also successful for most teens who have it to fix slow testicular growth.